6 min read
Why I Love Insurance: Carly’s Story
Why I Love Insurance: Carly’s Story by Carly Burnham Today we feature the story of our Co-Founder and Chief Editor Carly Burnham. You’ve...
5 min read
 Michelle Bothe
:
Sep 15, 2025 4:18:48 PM
Michelle Bothe
:
Sep 15, 2025 4:18:48 PM

Customer expectations are rising, and traditional staffing models are failing to scale efficiently. Insurers face five viable options for service delivery: (1) hire more humans, (2) outsource to another firm, (3) DIY with general AI tools like ChatGPT, (4) adopt a generic voice/CCaaS platform, or (5) implement insurance-native, omnichannel AI that talks and takes action within your systems while maintaining compliance. Among these, Option 5 provides the strongest balance of quality, cost efficiency, and risk control—if implemented with clear rules, integrations, and escalation paths.
| Model | Strengths | Best Fit | Where It Breaks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Human-Centric Team | Deep judgment, empathy, brand alignment | Low volume (<1k interactions/month), complex bespoke products | Linear cost curve, availability gaps, inconsistency, hiring/retention strain |
| Outsourcing | Cost-effective scalability, access to trained professionals | High-volume interactions, routine inquiries | Limited control over brand experience, potential quality inconsistencies |
| DIY AI (generic LLM) | High flexibility, IP learning, rapid prototyping | Teams with strong engineering resources | Integration burden, QA/hallucinations, compliance proof, ongoing MLOps |
| Generic Voice/CCaaS | Quick start, stable infrastructure | Commodity use cases, simple FAQs | Insurance context gap, limited system write-backs, customization ceilings |
| Insurance-Native AI | Compliance by design, end-to-end task completion, elastic scalability | Scaling MGAs/Carriers with multi-system operations | Higher upfront work, vendor dependency, change management |
Advantages
The human-centric model relies on hiring experienced insurance professionals to handle customer interactions. This approach offers several key benefits:
Challenges
Despite its strengths, the human-centric approach presents significant hurdles:
Advantages
Outsourcing customer service to a third-party firm offers scalable solutions for insurers facing high interaction volumes. Key benefits include:
Challenges
While outsourcing provides scalability, it also introduces risks:
Advantages
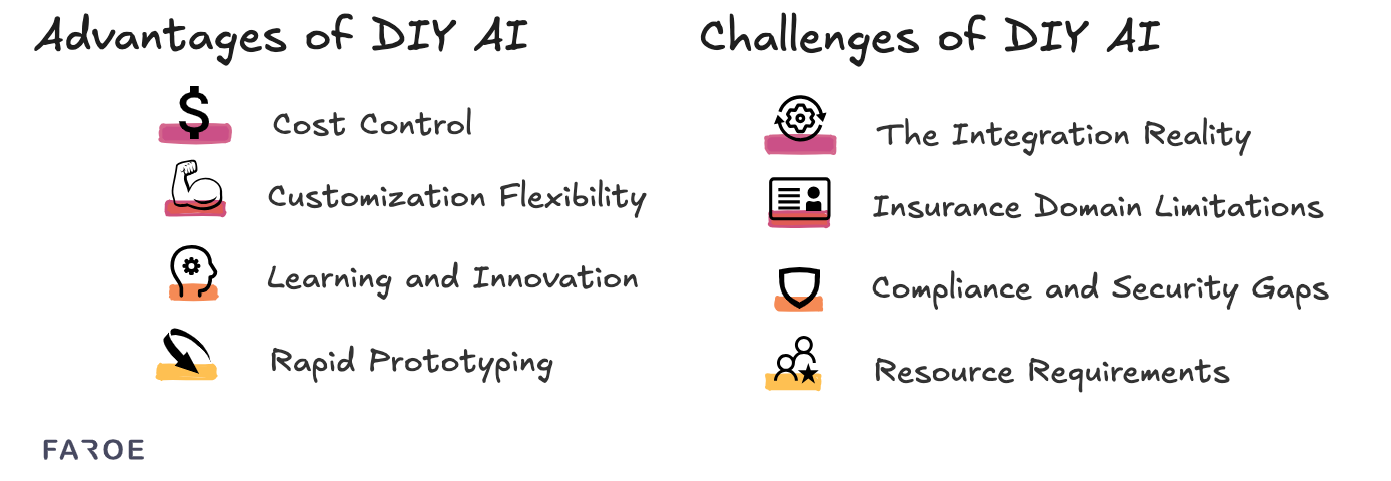
The democratization of AI tools like ChatGPT makes it tempting for insurers to build their own solutions internally. Benefits include:
Challenges
 DIY approaches come with hidden complexities:
DIY approaches come with hidden complexities:
Advantages
Platforms like RingCentral offer pre-built communication tools enhanced with basic AI capabilities for general business use cases:
Challenges
Generic platforms struggle to meet the unique needs of insurers:
Advantages
 Risk Management: Insurance-specific platforms understand the liability implications of AI in insurance contexts. They provide appropriate escalation triggers, human handoff protocols, and quality controls that protect both customer relationships and regulatory compliance.
Risk Management: Insurance-specific platforms understand the liability implications of AI in insurance contexts. They provide appropriate escalation triggers, human handoff protocols, and quality controls that protect both customer relationships and regulatory compliance.Challenges
While powerful, insurance-native platforms require careful implementation:
To choose the right approach for your organization, evaluate these criteria based on your operational realities:
 The customer service delivery challenge facing insurers isn’t temporary—it’s structural. Rising expectations for instant service paired with increasing costs demand a sustainable solution that balances automation with human expertise.
The customer service delivery challenge facing insurers isn’t temporary—it’s structural. Rising expectations for instant service paired with increasing costs demand a sustainable solution that balances automation with human expertise.
Among the five options outlined above, insurance-native omnichannel AI offers the most compelling mix of scalability, compliance strength, and cost efficiency—provided it’s implemented thoughtfully with clear rules and integrations.
Ultimately, the future belongs to MGAs, brokers, and carriers that can deliver exceptional customer experiences at scale while bending their cost curves downward through smart automation choices.
The choice isn’t human vs AI—it’s humans amplified by technology tailored specifically for the insurance industry’s unique needs.

6 min read
Why I Love Insurance: Carly’s Story by Carly Burnham Today we feature the story of our Co-Founder and Chief Editor Carly Burnham. You’ve...

4 min read
Dear Insurance Industry. . . a letter from those you serve by Ben Baker Photo by Suzy Hazelwood from Pexels If your customers were to write you...

3 min read
Insurers’ Dilemma: Mastery vs. Simplicity by Rock Schindler “Mastery isn’t making the simple complex – it is finding the elegant simplicity...